Archive
Cognitive capitalism chapter reworked
The Cognitive capitalism chapter of my evidence-based software engineering book took longer than expected to polish; in fact it got reworked, rather than polished (which still needs to happen, and there might be more text moving from other chapters).
Changing the chapter title, from Economics to Cognitive capitalism, helped clarify lots of decisions about the subject matter it ought to contain (the growth in chapter page count is more down to material moving from other chapters, than lots of new words from me).
I over-spent time down some interesting rabbit holes (e.g., real options), before realising that no public data was available, and unlikely to be available any time soon. Without data, there is not a lot that can be said in a data driven book.
Social learning is a criminally under researched topic in software engineering. Some very interesting work has been done by biologists (e.g., Joseph Henrich, and Kevin Laland), in the last 15 years; the field has taken off. There is a huge amount of social learning going on in software engineering, and virtually nobody is investigating it.
As always, if you know of any interesting software engineering data, please let me know.
Next, the Ecosystems chapter.
Evidence on the distribution and diversity of Christianity: 1900-2000
I recently read an article saying that Christianity had 33,830 denominations, with 150 having more than 1 million followers. Checking the references, World Christian Encyclopedia was cited as the source; David Barrett had spent 12 years traveling the world, talking to people to collect the data. An evidence-based man, after my own heart.
Checking the second-hand book sites, I found a copy of the 1982 edition available for a few pounds, and placed an order (this edition lists 20,800 denominations; how many more are there to be ‘discovered’).
The book that arrived was a bit larger than I had anticipated. This photograph shows just how large this book is, compared to other dead-tree data sources in my collection (on top, in red, is your regular 400 page book):

My interest in a data-driven discussion of the spread and diversity of religions, was driven by wanting ideas for measuring the spread and diversity of programming languages. Bill Kinnersley’s language list contains information on 2,500 programming languages, and there are probably an order of magnitude more languages waiting to be written about.
The data is available to researchers, but is not public 🙁
The World Christian Encyclopedia is way too detailed for my needs. I usually leave unwanted books on the book table of my local train station’s Coffee shop. I have left some unusual books there in the past, but this one feels like it needs a careful owner; I will see whether the local charity shop will take it in.
Background checks on pointer values being considered for C
DR 260 is a defect report submitted to WG14, the C Standards’ committee, in 2001 that was never resolved, then generally ignored for 10-years, then caught the attention of a research group a few years ago, and is now back on WG14’s agenda. The following discussion covers two of the three questions raised in the DR.
Consider the following fragment of code:
int *p, *q; p = malloc (sizeof (int)); assert (p != NULL); // Line A (free)(p); // Line B // more code q = malloc (sizeof (int)); assert (q != NULL); // Line C if (memcmp (&p, &q, sizeof p) == 0) // Line D {*p = 42; // Line E *q = 43;} // Line F |
Section 6.2.4p2 of the C Standard says:
“The value of a pointer becomes indeterminate when the object it points to (or just past) reaches the end of its lifetime.”
The call to free, on line B, ends the lifetime of the storage (allocated on line A) pointed to by p.
There are two proposed interpretations of the sentence, in 6.2.4p2.
- “becomes indeterminate” is treated as effectively storing a value in the pointer, i.e., some bit pattern denoting an indeterminate value. This interpretation requires that any other variables that had been assigned
p‘s value, prior to thefree, also have an indeterminate value stored into them, - the value held in the pointer is to be treated as an indeterminate value (for instance, a memory management unit may prevent any access to the corresponding storage).
What are the practical implications of the two options?
The call to malloc, on line C, could return a pointer to a location that is identical to the pointer returned by the first call to malloc, i.e., the second call might immediately reuse the free‘ed storage.
Effectively storing a value in the pointer, in response to the call to free means the subsequent call to memcmp would always return a non-zero value, and the questions raised below do not apply; it would be a nightmare to implement, especially in a multi-process environment.
If the sentence in section 6.2.4p2 is interpreted as treating the pointer value as indeterminate, then the definition of malloc needs to be updated to specify that all returned values are determinate, i.e., any indeterminacy that may exist gets removed before a value is returned (the memory management unit must allow read/write access to the storage).
The memcmp, on line D, does a byte-wise compare of the pointer values (a byte-wise compare side-steps indeterminate value issues). If the comparison is exact, an assignment is made via p, line E, and via q, line F.
Does the assignment via p result in undefined behavior, or is the conformance status of the code unaffected by its presence?
Nobody is impuning the conformance status of the assignment via q, on line F.
There are people who think that the assignment via p, on line E, should be treated as undefined behavior, despite the fact that the values of p and q are byte-wise identical. When this issue was first raised (by those trouble makers in the UK ;-), yours truly was less than enthusiastic, but there were enough knowledgeable people in the opposing camp to keep the ball rolling for a while.
The underlying issue some people have with some subsequent uses of p is its provenance, the activities it has previously been associated with.
Provenance can be included in the analysis process by associating a unique number with the address of every object, at the start of its lifetime; these p-numbers are not reused.
The value returned by the call to malloc, on line A, would include a pointer to the allocated storage, plus an associated p-number; the call on line C could return a pointer having the same value, but its p-number is required to be different. Implementations are not required to allocate any storage for p-numbers, treating them purely as conceptual quantities. Your author knows of two implementations that do allocate storage for p-numbers (in a private area), and track usage of p-numbers; the Model Implementation C Checker was validated as handling all of C90, and Cerberus which handles a substantial subset of C11, and I don’t believe that the other tools that check array bounds and use after free are based on provenance (corrections welcome).
If provenance is included as part of a pointer’s value, the behavior of operators needs to be expanded to handle the p-number (conceptual or not) component of a pointer.
The rules might specify that p-numbers are conceptually compared by the call to memcmp, on line C; hence p and q are considered to never compare equal. There is an existing practice of regarding byte compares as just that, i.e., no magic ever occurs when comparing bytes (otherwise known as objects having type unsigned char).
Having p-numbers be invisible to memcmp would be consistent with existing practice. The pointer indirection operation on line E (generating undefined behavior) is where p-numbers get involved and cause the undefined behavior to occur.
There are other situations where pointer values, that were once indeterminate, can appear to become ‘respectable’.
For a variable, defined in a function, “… its lifetime extends from entry into the block with which it is associated until execution of that block ends in any way.”; section 6.2.4p3.
In the following code:
int x; static int *p=&x; void f(int n) { int *q = &n; if (memcmp (&p, &q, sizeof p) == 0) *p = 0; p = &n; // assign an address that will soon cease to exist. } // Lifetime of pointed to object, n, terminates here int main(void) { f(1); // after this call, p has an indeterminate value f(2); } |
the pointer p has an indeterminate value after any call to f returns.
In many implementations, the second call to f will result in n having the same address it had on the first call, and memcmp will return zero.
Again, there are people who have an issue with the assignment involving p, because of its provenance.
One proposal to include provenance contains substantial changes to existing word in the C Standard. The rationale for is proposals looks more like a desire to change wording to make things clearer for those making the change, than a desire to address DR 260. Everybody thinks their proposed changes make the wording clearer (including yours truly), such claims are just marketing puff (and self-delusion); confirmation from the results of an A/B test would add substance to such claims.
It is probably possible to explicitly include support for provenance by making a small number of changes to existing wording.
Is the cost of supporting provenance (i.e., changing existing wording may introduce defects into the standard, the greater the amount of change the greater the likelihood of introducing defects), worth the benefits?
What are the benefits of introducing provenance?
Provenance makes it possible to easily specify that the uses of p, in the two previous examples (and a third given in DR 260), are undefined behavior (if that is WG14’s final decision).
Provenance also provides a model that might make it easier to reason about programs; it’s difficult to say one way or the other, without knowing what the model is.
Supporters claim that provenance would enable tool vendors to flag various snippets of code as suspicious. Tool vendors can already do this, they don’t need permission from the C Standard to flag anything they fancy.
The C Standard requires a conforming implementation to diagnose certain constructs. A conforming implementation can issue as many messages as it likes, for any other construct, e.g., for line A in the first example, a compiler might print “This is the 1,000,000’th call to malloc I have translated, ring this number to claim your prize!”
Before any changes are made to wording in the C Standard, WG14 needs to decide what the behavior should be for these examples; it could decide to continue ignoring them for another 20-years.
Once a decision is made, the next question is how to update wording in the standard to specify the behavior that has been decided on.
While provenance is an interesting idea, the benefits it provides appear to be not worth the cost of changing the C Standard.
A prisoner’s dilemma when agreeing to a management schedule
Two software developers, both looking for promotion/pay-rise by gaining favorable management reviews, are regularly given projects to complete by a date specified by management; the project schedules are sometimes unachievable, with probability 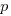 .
.
Let’s assume that both developers are simultaneously given a project, and the corresponding schedule. If the specified schedule is unachievable, High quality work can only be performed by asking for more time, otherwise performing Low quality work is the only way of meeting the schedule.
If either developer faces an unachievable deadline, they have to immediately decide whether to produce High or Low quality work. A High quality decision requires that they ask management for more time, and incur a penalty they perceive to be 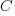 (saying they cannot meet the specified schedule makes them feel less worthy of a promotion/pay-rise); a Low quality decision is perceived to be likely to incur a penalty of
(saying they cannot meet the specified schedule makes them feel less worthy of a promotion/pay-rise); a Low quality decision is perceived to be likely to incur a penalty of 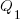 (because of its possible downstream impact on project completion), if one developer chooses Low, and
(because of its possible downstream impact on project completion), if one developer chooses Low, and 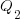 , if both developers choose Low. It is assumed that:
, if both developers choose Low. It is assumed that: 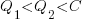 .
.
This is a prisoner’s dilemma problem. The following mathematical results are taken from: The Effects of Time Pressure on Quality in Software Development: An Agency Model, by Robert D. Austin (cannot find a downloadable pdf).
There are two Nash equilibriums, for the decision made by the two developers: Low-Low and High-High (i.e., both perform Low quality work, or both perform High quality work). Low-High is not a stable equilibrium, in that on the next iteration the two developers may switch their decisions.
High-High is a pure strategy (i.e., always use it), when: 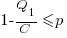
High-High is Pareto superior to Low-Low when: 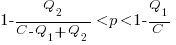
How might management use this analysis to increase the likelihood that a High-High quality decision is made?
Evidence shows that 50% of developer estimates, of task effort, underestimate the actual effort; there is sufficient uncertainty in software development that the likelihood of consistently produce accurate estimates is low (i.e., 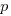 is a very fuzzy quantity). Managers wanting to increase the likelihood of a High-High decision could be generous when setting deadlines (e.g., multiple developer estimates by 200%, when setting the deadline for delivery), but managers are often under pressure from customers, to specify aggressively short deadlines.
is a very fuzzy quantity). Managers wanting to increase the likelihood of a High-High decision could be generous when setting deadlines (e.g., multiple developer estimates by 200%, when setting the deadline for delivery), but managers are often under pressure from customers, to specify aggressively short deadlines.
The penalty for a developer admitting that they cannot deliver by the specified schedule,  , could be set very low (e.g., by management not taking this factor into account when deciding developer promotion/pay-rise). But this might encourage developers to always give this response. If all developers mutually agreed to cooperate, to always give this response, none of them would lose relative to the others; but there is an incentive for the more capable developers to defect, and the less capable developers to want to use this strategy.
, could be set very low (e.g., by management not taking this factor into account when deciding developer promotion/pay-rise). But this might encourage developers to always give this response. If all developers mutually agreed to cooperate, to always give this response, none of them would lose relative to the others; but there is an incentive for the more capable developers to defect, and the less capable developers to want to use this strategy.
Regular code reviews are a possible technique for motivating High-High, by increasing the likelihood of any lone Low decision being detected. A Low-Low decision may go unreported by those involved.
To summarise: an interesting analysis that appears to have no practical use, because reasonable estimates of the values of the variables involved are unavailable.
C Standard meeting, April-May 2019
I was at the ISO C language committee meeting, WG14, in London this week (apart from the few hours on Friday morning, which was scheduled to be only slightly longer than my commute to the meeting would have been).
It has been three years since the committee last met in London (the meeting was planned for Germany, but there was a hosting issue, and Germany are hosting next year), and around 20 people attended, plus 2-5 people dialing in. Some regular attendees were not in the room because of schedule conflicts; nine of those present were in London three years ago, and I had met three of those present (this week) at WG14 meetings prior to the last London meeting. I had thought that Fred Tydeman was the longest serving member in the room, but talking to Fred I found out that I was involved a few years earlier than him (our convenor is also a long-time member); Fred has attended more meeting than me, since I stopped being a regular attender 10 years ago. Tom Plum, who dialed in, has been a member from the beginning, and Larry Jones, who dialed in, predates me. There are still original committee members active on the WG14 mailing list.
Having so many relatively new meeting attendees is a good thing, in that they are likely to be keen and willing to do things; it’s also a bad thing for exactly the same reason (i.e., if it not really broken, don’t fix it).
The bulk of committee time was spent discussing the proposals contains in papers that have been submitted (listed in the agenda). The C Standard is currently being revised, WG14 are working to produce C2X. If a person wants the next version of the C Standard to support particular functionality, then they have to submit a paper specifying the desired functionality; for any proposal to have any chance of success, the interested parties need to turn up at multiple meetings, and argue for it.
There were three common patterns in the proposals discussed (none of these patterns are unique to the London meeting):
- change existing wording, based on the idea that the change will stop compilers generating code that the person making the proposal considers to be undesirable behavior. Some proposals fitting this pattern were for niche uses, with alternative solutions available. If developers don’t have the funding needed to influence the behavior of open source compilers, submitting a proposal to WG14 offers a low cost route. Unless the proposal is a compelling use case, affecting lots of developers, WG14’s incentive is to not adopt the proposal (accepting too many proposals will only encourage trolls),
- change/add wording to be compatible with C++. There are cost advantages, for vendors who have to support C and C++ products, to having the two language be as mutually consistent as possible. Embedded systems are a major market for C, but this market is not nearly as large for C++ (because of the much larger overhead required to support C++). I pointed out that WG14 needs to be careful about alienating a significant user base, by slavishly following C++; the C language needs to maintain a separate identity, for long term survival,
- add a new function to the C library, based on its existence in another standard. Why add new functions to the C library? In the case of math functions, it’s to increase the likelihood that the implementation will be correct (maths functions often have dark corners that are difficult to get right), and for string functions it’s the hope that compilers will do magic to turn a function call directly into inline code. The alternative argument is not to add any new functions, because the common cases are already covered, and everything else is niche usage.
At the 2016 London meeting Peter Sewell gave a presentation on the Cerberus group’s work on a formal definition of C; this work has resulted in various papers questioning the interpretation of wording in the standard, i.e., possible ambiguities or inconsistencies. At this meeting the submitted papers focused on pointer provenance, and I was expecting to hear about the fancy optimizations this work would enable (which would be a major selling point of any proposal). No such luck, the aim of the work was stated as clearly specifying the behavior (a worthwhile aim), with no major new optimizations being claimed (formal methods researchers often oversell their claims, Peter is at the opposite end of the spectrum and could do with an injection of some positive advertising). Clarifying behavior is a worthwhile aim, but not at the cost of major changes to existing wording. I have had plenty of experience of asking WG14 for clarification of existing (what I thought to be ambiguous) wording, only to be told that the existing wording was clear and not ambiguous (to those reviewing my proposed defect). I wonder how many of the wording ambiguities that the Cerberus group claim to have found would be accepted by WG14 as a defect that required a wording change?
Winner of the best pub quiz question: Does the C Standard require an implementation to be able to exactly represent floating-point zero? No, but it is now required in C2X. Do any existing conforming implementations not support an exact representation for floating-point zero? There are processors that use a logarithmic representation for floating-point, but I don’t know if any conforming implementation exists for such systems; all implementations I know of support an exact representation for floating-point zero. Logarithmic representation could handle zero using a special bit pattern, with cpu instructions doing the right thing when operating on this bit pattern, e.g., 0.0+X == X, (I wonder how much code would break, if the compiler mapped the literal 0.0 to the representable value nearest to zero).
Winner of the best good intentions corrupted by the real world: intmax_t, an integer type capable of representing any value of any signed integer type (i.e., a largest representable integer type). The concept of a unique largest has issues in a world that embraces diversity.
Today’s C development environment is very different from 25 years ago, let alone 40 years ago. The number of compilers in active use has decreased by almost two orders of magnitude, the number of commonly encountered distinct processors has shrunk, the number of very distinct operating systems has shrunk. While it is not a monoculture, things appear to be heading in that direction.
The relevance of WG14 decreases, as the number of independent C compilers, in widespread use, decreases.
What is the purpose of a C Standard in today’s world? If it were not already a standard, I don’t think a committee would be set up to standardize the language today.
Is the role of WG14 now, the arbiter of useful common practice across widely used compilers? Documenting decisions in revisions of the C Standard.
Work on the Cobol Standard ran for almost 60-years; WG14 has to be active for another 20-years to equal this.
Recent Comments